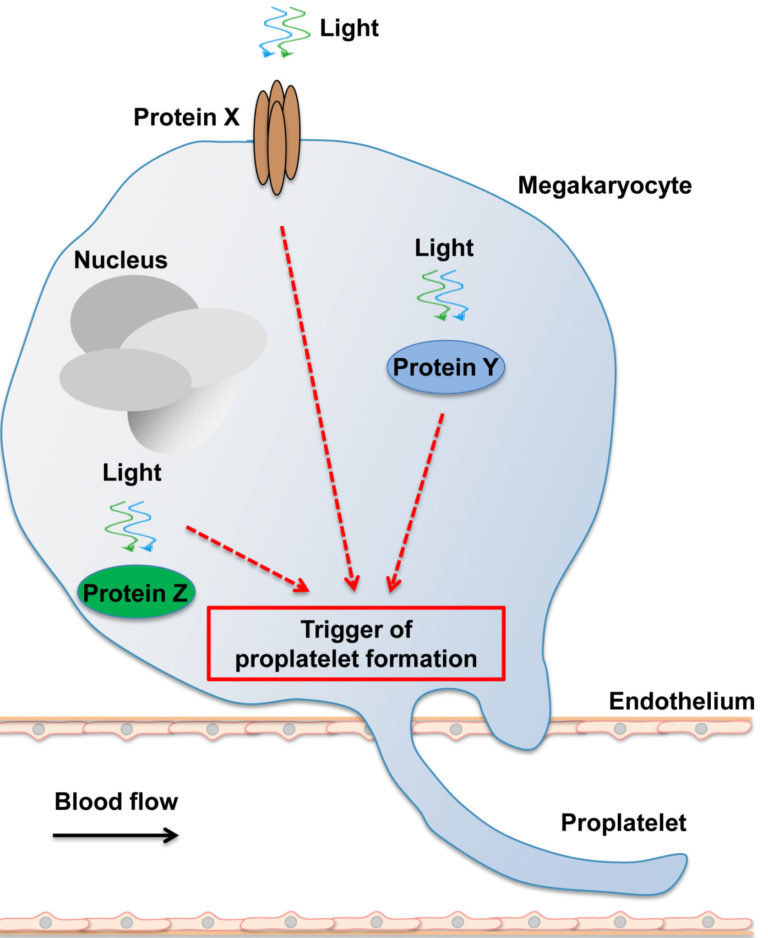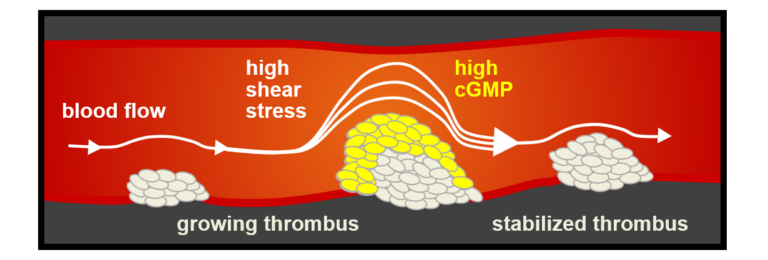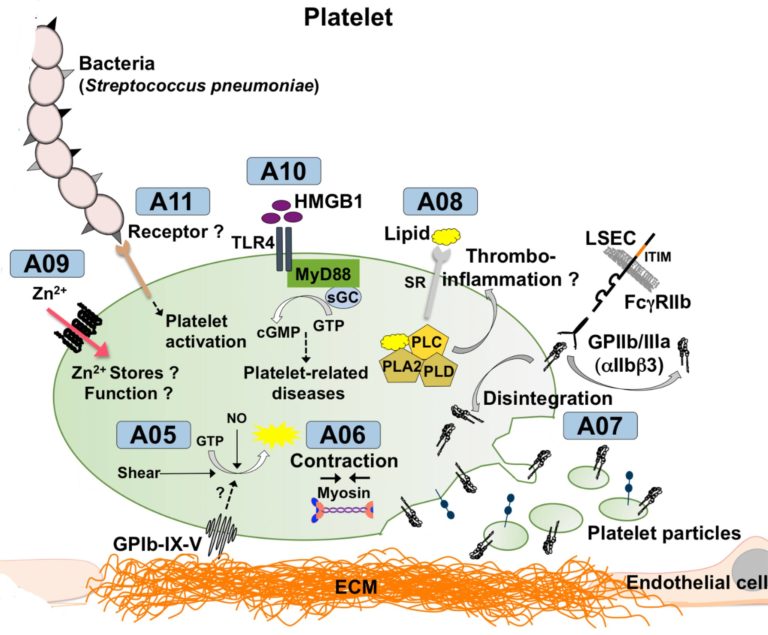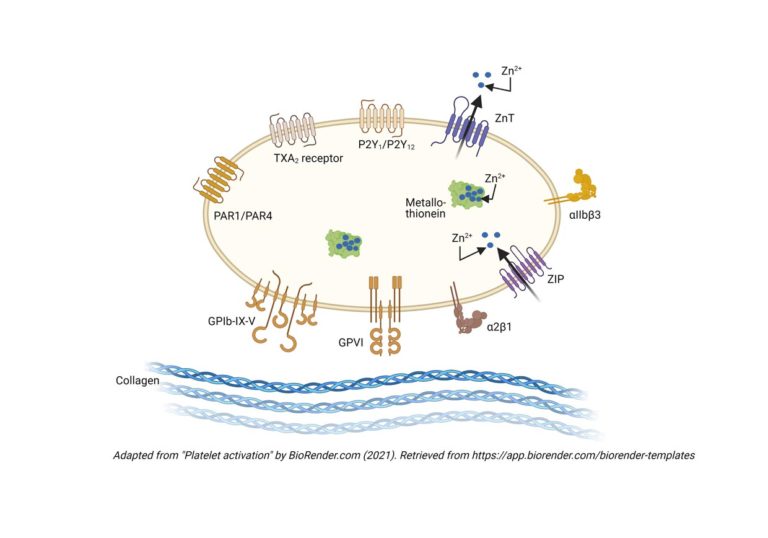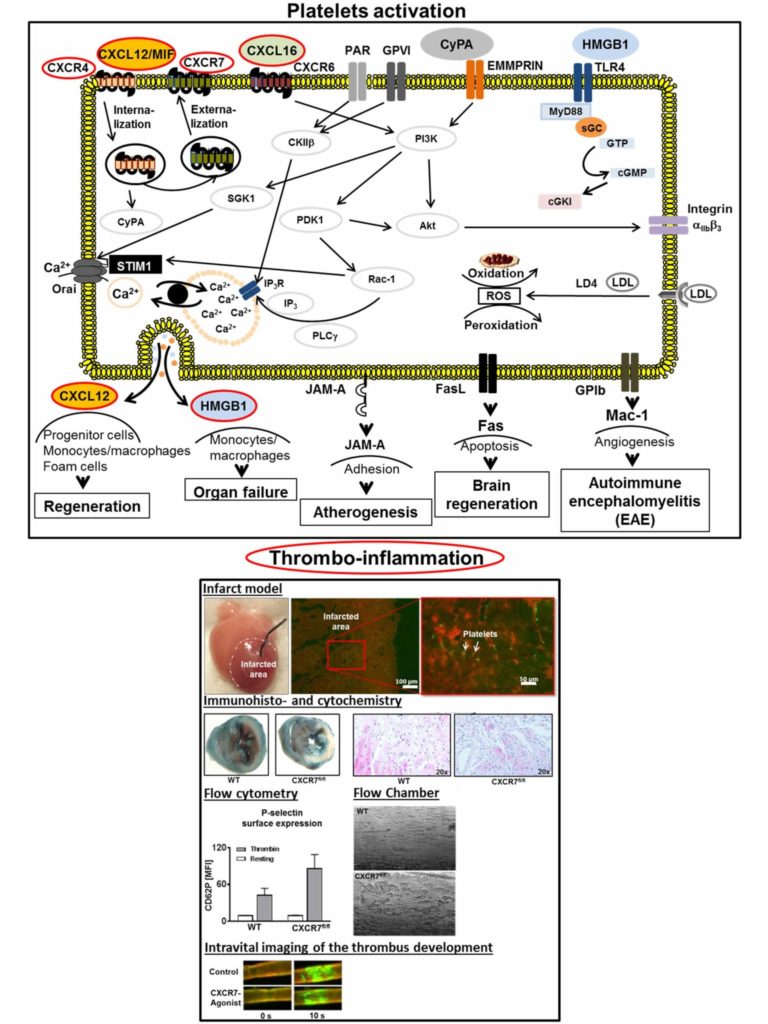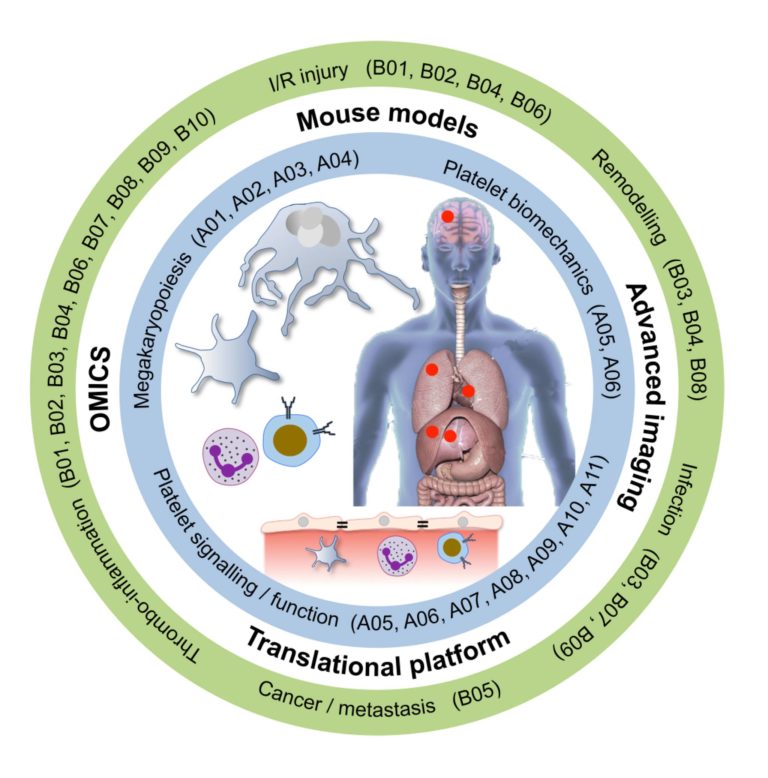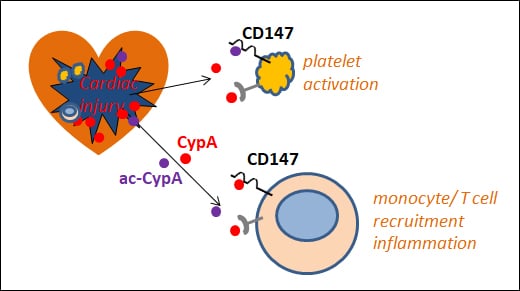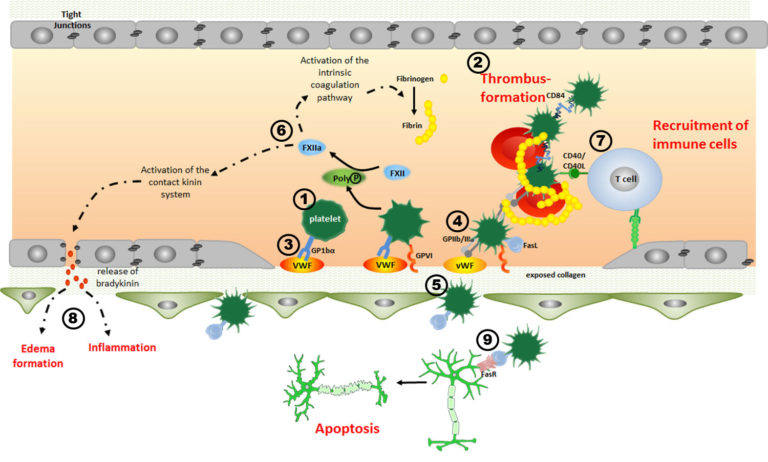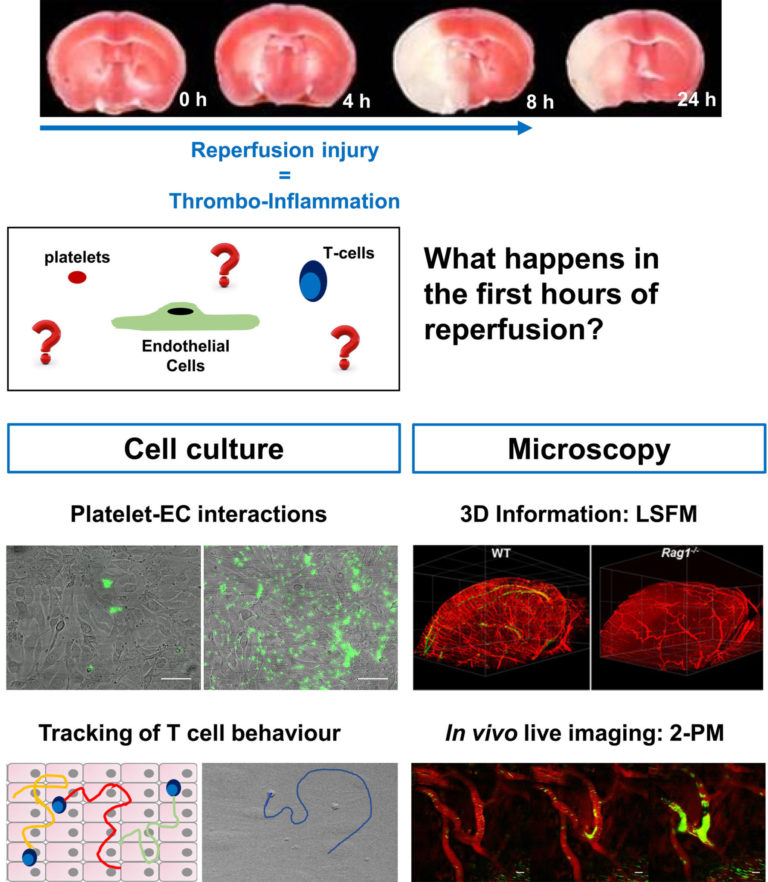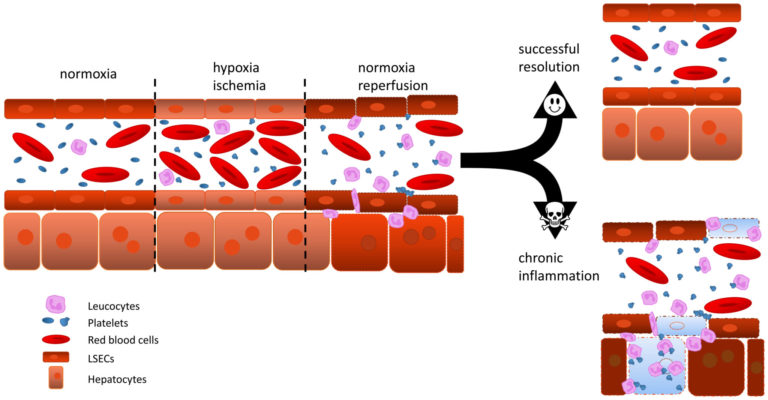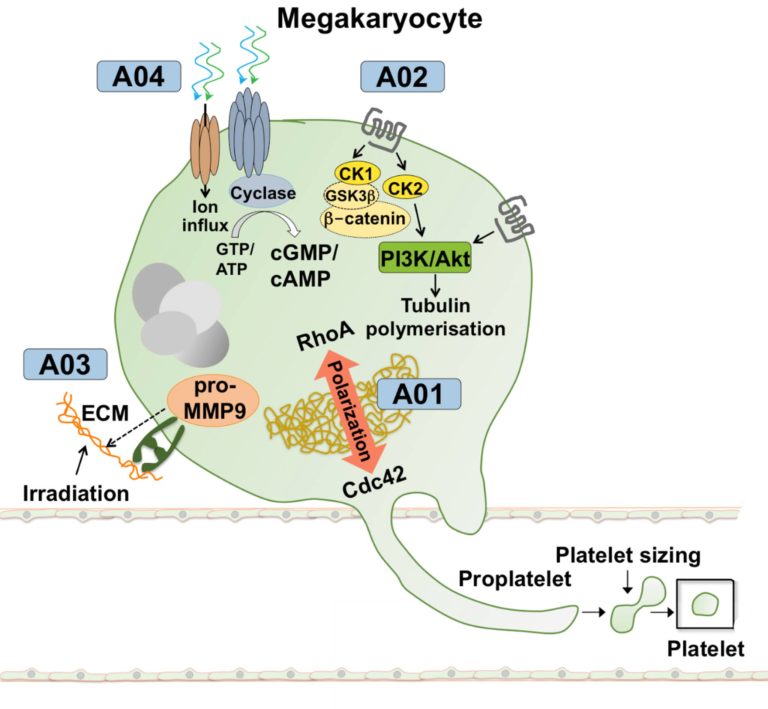
A01 – Mechanisms of megakaryocyte polarisation and platelet biogenesis
Blood platelets are anucleated cell fragments that are essential for blood clotting. They are produced by large precursor cells residing in the bone marrow (BM), the megakaryocytes (MKs). Platelet biogenesis